license: apache-2.0
language:
- en
pipeline_tag: text-generation
tags:
- multimodal
base_model: Qwen/Qwen2-VL-7B-Instruct-GPTQ-Int8
Qwen2-VL-7B-Instruct-GPTQ-Int8
Introduction
We're excited to unveil Qwen2-VL, the latest iteration of our Qwen-VL model, representing nearly a year of innovation.
What’s New in Qwen2-VL?
Key Enhancements:
Enhanced Image Comprehension: We've significantly improved the model's ability to understand and interpret visual information, setting new benchmarks across key performance metrics.
Advanced Video Understanding: Qwen2-VL now features superior online streaming capabilities, enabling real-time analysis of dynamic video content with remarkable accuracy.
Integrated Visual Agent Functionality: Our model now seamlessly incorporates sophisticated system integration, transforming Qwen2-VL into a powerful visual agent capable of complex reasoning and decision-making.
Expanded Multilingual Support: We've broadened our language capabilities to better serve a diverse global user base, making Qwen2-VL more accessible and effective across different linguistic contexts.
Model Architecture Updates:
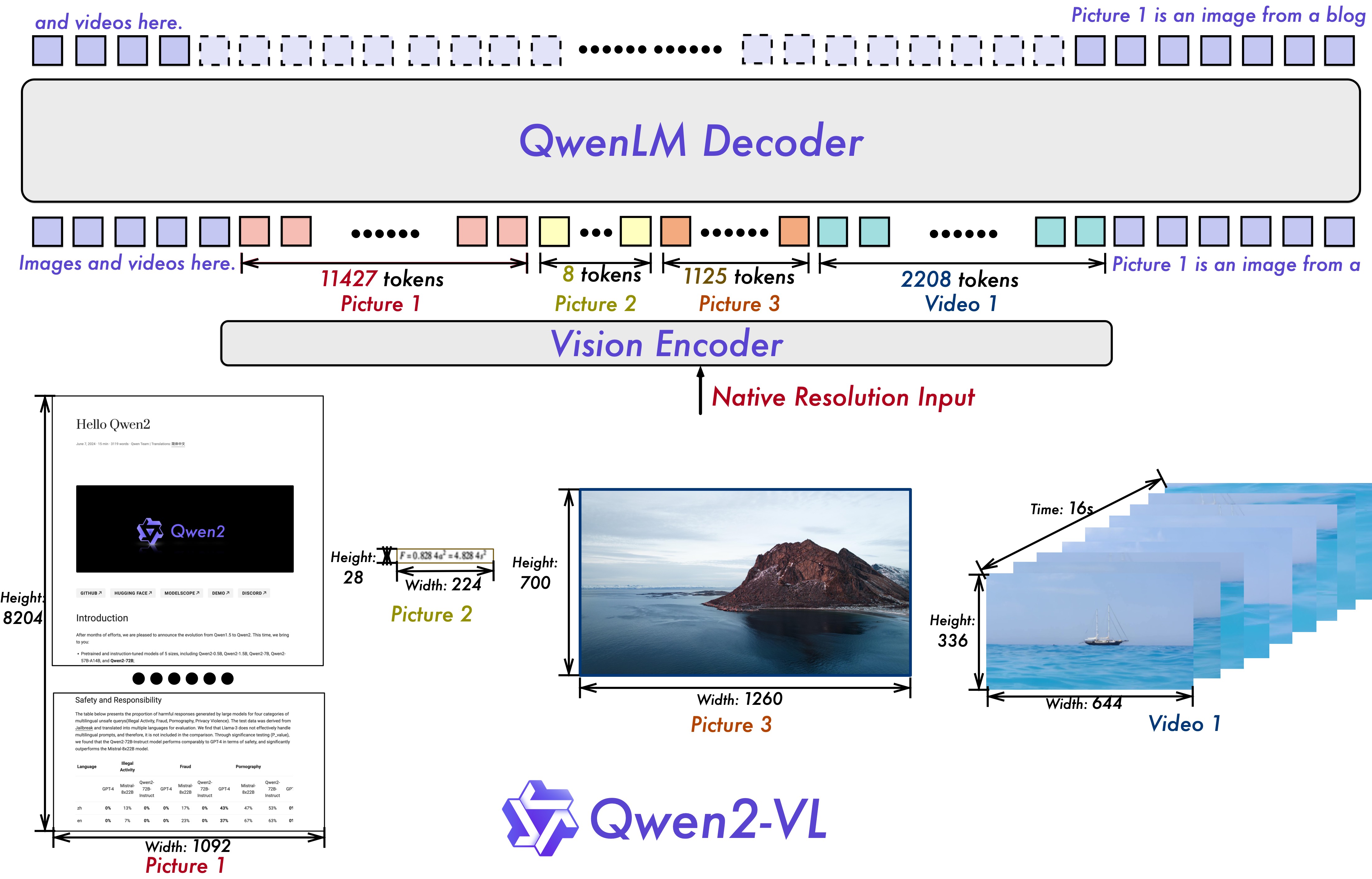
Naive Dynamic Resolution: Unlike before, Qwen2-VL can handle arbitrary image resolutions, mapping them into a dynamic number of visual tokens, offering a more human-like visual processing experience.
Multimodal Rotary Position Embedding (M-ROPE): Decomposes positional embedding into parts to capture 1D textual, 2D visual, and 3D video positional information, enhancing its multimodal processing capabilities.
We have three models with 2, 7 and 72 billion parameters. This repo contains the instruction-tuned 7B Qwen2-VL model. For more information, visit our Blog and GitHub.
Benchmark
Performance of Quantized Models
This section reports the generation performance of quantized models (including GPTQ and AWQ) of the Qwen2-VL series. Specifically, we report:
- MMMU_VAL (Accuracy)
- DocVQA_VAL (Accuracy)
- MMBench_DEV_EN (Accuracy)
- MathVista_MINI (Accuracy)
We use VLMEvalkit to evaluate all models.
| Model Size | Quantization | MMMU | DocVQA | MMBench | MathVista |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qwen2-VL-7B-Instruct | BF16 (🤗🤖) |
53.77 | 93.89 | 81.78 | 58.20 |
| GPTQ-Int8 (🤗🤖) |
53.00 | 93.94 | 82.38 | 57.90 | |
| GPTQ-Int4 (🤗🤖) |
52.55 | 93.16 | 81.27 | 60.30 | |
| AWQ (🤗🤖) |
53.66 | 93.10 | 81.61 | 56.80 |
Speed Benchmark
This section reports the speed performance of bf16 models, quantized models (including GPTQ-Int4, GPTQ-Int8 and AWQ) of the Qwen2-VL series. Specifically, we report the inference speed (tokens/s) as well as memory footprint (GB) under the conditions of different context lengths.
The environment of the evaluation with huggingface transformers is:
- NVIDIA A100 80GB
- CUDA 11.8
- Pytorch 2.2.1+cu118
- Flash Attention 2.6.1
- Transformers 4.38.2
- AutoGPTQ 0.6.0+cu118
- AutoAWQ 0.2.5+cu118 (autoawq_kernels 0.0.6+cu118)
Note:
We use the batch size of 1 and the least number of GPUs as possible for the evalution.
We test the speed and memory of generating 2048 tokens with the input lengths of 1, 6144, 14336, 30720, 63488, and 129024 tokens (>32k is only avaliable for Qwen2-72B-Instuct and Qwen2-7B-Instuct).
7B (transformers)
| Model | Input Length | Quantization | GPU Num | Speed(tokens/s) | GPU Memory(GB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qwen2-VL-7B-Instruct | 1 | BF16 | 1 | 39.02 | 16.07 |
| GPTQ-Int8 | 1 | 31.60 | 10.11 | ||
| GPTQ-Int4 | 1 | 42.76 | 7.20 | ||
| AWQ | 1 | 32.08 | 7.07 | ||
| 6144 | BF16 | 1 | 38.75 | 21.56 | |
| GPTQ-Int8 | 1 | 31.31 | 15.61 | ||
| GPTQ-Int4 | 1 | 39.75 | 12.69 | ||
| AWQ | 1 | 32.66 | 12.56 | ||
| 14336 | BF16 | 1 | 30.65 | 29.07 | |
| GPTQ-Int8 | 1 | 27.96 | 23.11 | ||
| GPTQ-Int4 | 1 | 29.72 | 20.20 | ||
| AWQ | 1 | 31.42 | 20.07 | ||
| 30720 | BF16 | 1 | 19.53 | 44.08 | |
| GPTQ-Int8 | 1 | 18.37 | 38.13 | ||
| GPTQ-Int4 | 1 | 19.15 | 35.22 | ||
| AWQ | 1 | 19.95 | 35.08 |
Requirements
The code of Qwen2-VL has been in the latest Hugging face transformers and we advise you to build from source with command pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers, or you might encounter the following error:
KeyError: 'qwen2_vl'
Quickstart
We offer a toolkit to help you handle various types of visual input more conveniently, as if you were using an API. This includes base64, URLs, and interleaved images and videos. You can install it using the following command:
pip install qwen-vl-utils
Here we show a code snippet to show you how to use the chat model with transformers and qwen_vl_utils:
from transformers import Qwen2VLForConditionalGeneration, AutoTokenizer, AutoProcessor
from qwen_vl_utils import process_vision_info
# default: Load the model on the available device(s)
model = Qwen2VLForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(
"Qwen/Qwen2-VL-7B-Instruct-GPTQ-Int8", torch_dtype="auto", device_map="auto"
)
# We recommend enabling flash_attention_2 for better acceleration and memory saving, especially in multi-image and video scenarios.
# model = Qwen2VLForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(
# "Qwen/Qwen2-VL-7B-Instruct-GPTQ-Int8",
# torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
# attn_implementation="flash_attention_2",
# device_map="auto",
# )
# default processer
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("Qwen/Qwen2-VL-7B-Instruct-GPTQ-Int8")
# The default range for the number of visual tokens per image in the model is 4-16384. You can set min_pixels and max_pixels according to your needs, such as a token count range of 256-1280, to balance speed and memory usage.
# min_pixels = 256*28*28
# max_pixels = 1280*28*28
# processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("Qwen/Qwen2-VL-7B-Instruct-GPTQ-Int8", min_pixels=min_pixels, max_pixels=max_pixels)
messages = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{
"type": "image",
"image": "https://qianwen-res.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/Qwen-VL/assets/demo.jpeg",
},
{"type": "text", "text": "Describe this image."},
],
}
]
# Preparation for inference
text = processor.apply_chat_template(
messages, tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=True
)
image_inputs, video_inputs = process_vision_info(messages)
inputs = processor(
text=[text],
images=image_inputs,
videos=video_inputs,
padding=True,
return_tensors="pt",
)
inputs = inputs.to("cuda")
# Inference: Generation of the output
generated_ids = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=128)
generated_ids_trimmed = [
out_ids[len(in_ids) :] for in_ids, out_ids in zip(inputs.input_ids, generated_ids)
]
output_text = processor.batch_decode(
generated_ids_trimmed, skip_special_tokens=True, clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False
)
print(output_text)
Without qwen_vl_utils
from PIL import Image
import requests
import torch
from torchvision import io
from typing import Dict
from transformers import Qwen2VLForConditionalGeneration, AutoTokenizer, AutoProcessor
# Load the model in half-precision on the available device(s)
model = Qwen2VLForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(
"Qwen/Qwen2-VL-7B-Instruct-GPTQ-Int8", torch_dtype="auto", device_map="auto"
)
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("Qwen/Qwen2-VL-7B-Instruct-GPTQ-Int8")
# Image
url = "https://qianwen-res.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/Qwen-VL/assets/demo.jpeg"
image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
conversation = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{
"type": "image",
},
{"type": "text", "text": "Describe this image."},
],
}
]
# Preprocess the inputs
text_prompt = processor.apply_chat_template(conversation, add_generation_prompt=True)
# Excepted output: '<|im_start|>system\nYou are a helpful assistant.<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>user\n<|vision_start|><|image_pad|><|vision_end|>Describe this image.<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>assistant\n'
inputs = processor(
text=[text_prompt], images=[image], padding=True, return_tensors="pt"
)
inputs = inputs.to("cuda")
# Inference: Generation of the output
output_ids = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=128)
generated_ids = [
output_ids[len(input_ids) :]
for input_ids, output_ids in zip(inputs.input_ids, output_ids)
]
output_text = processor.batch_decode(
generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True, clean_up_tokenization_spaces=True
)
print(output_text)
Multi image inference
# Messages containing multiple images and a text query
messages = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "image", "image": "file:///path/to/image1.jpg"},
{"type": "image", "image": "file:///path/to/image2.jpg"},
{"type": "text", "text": "Identify the similarities between these images."},
],
}
]
# Preparation for inference
text = processor.apply_chat_template(
messages, tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=True
)
image_inputs, video_inputs = process_vision_info(messages)
inputs = processor(
text=[text],
images=image_inputs,
videos=video_inputs,
padding=True,
return_tensors="pt",
)
inputs = inputs.to("cuda")
# Inference
generated_ids = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=128)
generated_ids_trimmed = [
out_ids[len(in_ids) :] for in_ids, out_ids in zip(inputs.input_ids, generated_ids)
]
output_text = processor.batch_decode(
generated_ids_trimmed, skip_special_tokens=True, clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False
)
print(output_text)
Video inference
# Messages containing a images list as a video and a text query
messages = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{
"type": "video",
"video": [
"file:///path/to/frame1.jpg",
"file:///path/to/frame2.jpg",
"file:///path/to/frame3.jpg",
"file:///path/to/frame4.jpg",
],
"fps": 1.0,
},
{"type": "text", "text": "Describe this video."},
],
}
]
# Messages containing a video and a text query
messages = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{
"type": "video",
"video": "file:///path/to/video1.mp4",
"max_pixels": 360 * 420,
"fps": 1.0,
},
{"type": "text", "text": "Describe this video."},
],
}
]
# Preparation for inference
text = processor.apply_chat_template(
messages, tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=True
)
image_inputs, video_inputs = process_vision_info(messages)
inputs = processor(
text=[text],
images=image_inputs,
videos=video_inputs,
padding=True,
return_tensors="pt",
)
inputs = inputs.to("cuda")
# Inference
generated_ids = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=128)
generated_ids_trimmed = [
out_ids[len(in_ids) :] for in_ids, out_ids in zip(inputs.input_ids, generated_ids)
]
output_text = processor.batch_decode(
generated_ids_trimmed, skip_special_tokens=True, clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False
)
print(output_text)
Batch inference
# Sample messages for batch inference
messages1 = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "image", "image": "file:///path/to/image1.jpg"},
{"type": "image", "image": "file:///path/to/image2.jpg"},
{"type": "text", "text": "What are the common elements in these pictures?"},
],
}
]
messages2 = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "Who are you?"},
]
# Combine messages for batch processing
messages = [messages1, messages1]
# Preparation for batch inference
texts = [
processor.apply_chat_template(msg, tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=True)
for msg in messages
]
image_inputs, video_inputs = process_vision_info(messages)
inputs = processor(
text=texts,
images=image_inputs,
videos=video_inputs,
padding=True,
return_tensors="pt",
)
inputs = inputs.to("cuda")
# Batch Inference
generated_ids = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=128)
generated_ids_trimmed = [
out_ids[len(in_ids) :] for in_ids, out_ids in zip(inputs.input_ids, generated_ids)
]
output_texts = processor.batch_decode(
generated_ids_trimmed, skip_special_tokens=True, clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False
)
print(output_texts)
More Usage Tips
For input images, we support local files, base64, and URLs. For videos, we currently only support local files.
# You can directly insert a local file path, a URL, or a base64-encoded image into the position where you want in the text.
## Local file path
messages = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "image", "image": "file:///path/to/your/image.jpg"},
{"type": "text", "text": "Describe this image."},
],
}
]
## Image URL
messages = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "image", "image": "http://path/to/your/image.jpg"},
{"type": "text", "text": "Describe this image."},
],
}
]
## Base64 encoded image
messages = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "image", "image": "data:image;base64,/9j/..."},
{"type": "text", "text": "Describe this image."},
],
}
]
Image Resolution for performance boost
The model supports a wide range of resolution inputs. By default, it uses the native resolution for input, but higher resolutions can enhance performance at the cost of more computation. Users can set the minimum and maximum number of pixels to achieve an optimal configuration for their needs, such as a token count range of 256-1280, to balance speed and memory usage.
min_pixels = 256 * 28 * 28
max_pixels = 1280 * 28 * 28
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(
"Qwen/Qwen2-VL-7B-Instruct-GPTQ-Int8", min_pixels=min_pixels, max_pixels=max_pixels
)
Besides, We provide two methods for fine-grained control over the image size input to the model:
Define min_pixels and max_pixels: Images will be resized to maintain their aspect ratio within the range of min_pixels and max_pixels.
Specify exact dimensions: Directly set
resized_heightandresized_width. These values will be rounded to the nearest multiple of 28.
# min_pixels and max_pixels
messages = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{
"type": "image",
"image": "file:///path/to/your/image.jpg",
"resized_height": 280,
"resized_width": 420,
},
{"type": "text", "text": "Describe this image."},
],
}
]
# resized_height and resized_width
messages = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{
"type": "image",
"image": "file:///path/to/your/image.jpg",
"min_pixels": 50176,
"max_pixels": 50176,
},
{"type": "text", "text": "Describe this image."},
],
}
]
Limitations
While Qwen2-VL are applicable to a wide range of visual tasks, it is equally important to understand its limitations. Here are some known restrictions:
- Lack of Audio Support: The current model does not comprehend audio information within videos.
- Data timeliness: Our image dataset is updated until June 2023, and information subsequent to this date may not be covered.
- Constraints in Individuals and Intellectual Property (IP): The model's capacity to recognize specific individuals or IPs is limited, potentially failing to comprehensively cover all well-known personalities or brands.
- Limited Capacity for Complex Instruction: When faced with intricate multi-step instructions, the model's understanding and execution capabilities require enhancement.
- Insufficient Counting Accuracy: Particularly in complex scenes, the accuracy of object counting is not high, necessitating further improvements.
- Weak Spatial Reasoning Skills: Especially in 3D spaces, the model's inference of object positional relationships is inadequate, making it difficult to precisely judge the relative positions of objects.
These limitations serve as ongoing directions for model optimization and improvement, and we are committed to continually enhancing the model's performance and scope of application.
Citation
If you find our work helpful, feel free to give us a cite.
@article{Qwen2-VL,
title={Qwen2-VL},
author={Qwen team},
year={2024}
}
@article{Qwen-VL,
title={Qwen-VL: A Versatile Vision-Language Model for Understanding, Localization, Text Reading, and Beyond},
author={Bai, Jinze and Bai, Shuai and Yang, Shusheng and Wang, Shijie and Tan, Sinan and Wang, Peng and Lin, Junyang and Zhou, Chang and Zhou, Jingren},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.12966},
year={2023}
}