base_model: https://huggingface.co/Open-Orca/LlongOrca-7B-16k
datasets:
- Open-Orca/OpenOrca
inference: false
language:
- en
library_name: transformers
license: llama2
model_creator: Open-Orca
model_name: LlongOrca 7B 16K
model_type: llama
pipeline_tag: text-generation
prompt_template: |
<|im_start|>system
{system_message}<|im_end|>
<|im_start|>user
{prompt}<|im_end|>
<|im_start|>assistant
quantized_by: TheBloke

TheBloke's LLM work is generously supported by a grant from andreessen horowitz (a16z)
LlongOrca 7B 16K - AWQ
- Model creator: Open-Orca
- Original model: LlongOrca 7B 16K
Description
This repo contains AWQ model files for Open-Orca's LlongOrca 7B 16K.
About AWQ
AWQ is an efficient, accurate and blazing-fast low-bit weight quantization method, currently supporting 4-bit quantization. Compared to GPTQ, it offers faster Transformers-based inference.
It is also now supported by continuous batching server vLLM, allowing use of AWQ models for high-throughput concurrent inference in multi-user server scenarios. Note that, at the time of writing, overall throughput is still lower than running vLLM with unquantised models, however using AWQ enables using much smaller GPUs which can lead to easier deployment and overall cost savings. For example, a 70B model can be run on 1 x 48GB GPU instead of 2 x 80GB.
Repositories available
- AWQ model(s) for GPU inference.
- GPTQ models for GPU inference, with multiple quantisation parameter options.
- 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 8-bit GGUF models for CPU+GPU inference
- Open-Orca's original unquantised fp16 model in pytorch format, for GPU inference and for further conversions
Prompt template: ChatML
<|im_start|>system
{system_message}<|im_end|>
<|im_start|>user
{prompt}<|im_end|>
<|im_start|>assistant
Provided files and AWQ parameters
For my first release of AWQ models, I am releasing 128g models only. I will consider adding 32g as well if there is interest, and once I have done perplexity and evaluation comparisons, but at this time 32g models are still not fully tested with AutoAWQ and vLLM.
Models are released as sharded safetensors files.
Serving this model from vLLM
Documentation on installing and using vLLM can be found here.
- When using vLLM as a server, pass the
--quantization awqparameter, for example:
python3 python -m vllm.entrypoints.api_server --model TheBloke/LlongOrca-7B-16K-AWQ --quantization awq
When using vLLM from Python code, pass the quantization=awq parameter, for example:
from vllm import LLM, SamplingParams
prompts = [
"Hello, my name is",
"The president of the United States is",
"The capital of France is",
"The future of AI is",
]
sampling_params = SamplingParams(temperature=0.8, top_p=0.95)
llm = LLM(model="TheBloke/LlongOrca-7B-16K-AWQ", quantization="awq")
outputs = llm.generate(prompts, sampling_params)
# Print the outputs.
for output in outputs:
prompt = output.prompt
generated_text = output.outputs[0].text
print(f"Prompt: {prompt!r}, Generated text: {generated_text!r}")
How to use this AWQ model from Python code
Install the necessary packages
Requires: AutoAWQ 0.0.2 or later
pip3 install autoawq
If you have problems installing AutoAWQ using the pre-built wheels, install it from source instead:
pip3 uninstall -y autoawq
git clone https://github.com/casper-hansen/AutoAWQ
cd AutoAWQ
pip3 install .
You can then try the following example code
from awq import AutoAWQForCausalLM
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
model_name_or_path = "TheBloke/LlongOrca-7B-16K-AWQ"
# Load model
model = AutoAWQForCausalLM.from_quantized(model_name_or_path, fuse_layers=True,
trust_remote_code=False, safetensors=True)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path, trust_remote_code=False)
prompt = "Tell me about AI"
prompt_template=f'''<|im_start|>system
{system_message}<|im_end|>
<|im_start|>user
{prompt}<|im_end|>
<|im_start|>assistant
'''
print("\n\n*** Generate:")
tokens = tokenizer(
prompt_template,
return_tensors='pt'
).input_ids.cuda()
# Generate output
generation_output = model.generate(
tokens,
do_sample=True,
temperature=0.7,
top_p=0.95,
top_k=40,
max_new_tokens=512
)
print("Output: ", tokenizer.decode(generation_output[0]))
# Inference can also be done using transformers' pipeline
from transformers import pipeline
print("*** Pipeline:")
pipe = pipeline(
"text-generation",
model=model,
tokenizer=tokenizer,
max_new_tokens=512,
do_sample=True,
temperature=0.7,
top_p=0.95,
top_k=40,
repetition_penalty=1.1
)
print(pipe(prompt_template)[0]['generated_text'])
Compatibility
The files provided are tested to work with AutoAWQ, and vLLM.
Huggingface Text Generation Inference (TGI) is not yet compatible with AWQ, but a PR is open which should bring support soon: TGI PR #781.
Discord
For further support, and discussions on these models and AI in general, join us at:
Thanks, and how to contribute
Thanks to the chirper.ai team!
Thanks to Clay from gpus.llm-utils.org!
I've had a lot of people ask if they can contribute. I enjoy providing models and helping people, and would love to be able to spend even more time doing it, as well as expanding into new projects like fine tuning/training.
If you're able and willing to contribute it will be most gratefully received and will help me to keep providing more models, and to start work on new AI projects.
Donaters will get priority support on any and all AI/LLM/model questions and requests, access to a private Discord room, plus other benefits.
- Patreon: https://patreon.com/TheBlokeAI
- Ko-Fi: https://ko-fi.com/TheBlokeAI
Special thanks to: Aemon Algiz.
Patreon special mentions: Alicia Loh, Stephen Murray, K, Ajan Kanaga, RoA, Magnesian, Deo Leter, Olakabola, Eugene Pentland, zynix, Deep Realms, Raymond Fosdick, Elijah Stavena, Iucharbius, Erik Bjäreholt, Luis Javier Navarrete Lozano, Nicholas, theTransient, John Detwiler, alfie_i, knownsqashed, Mano Prime, Willem Michiel, Enrico Ros, LangChain4j, OG, Michael Dempsey, Pierre Kircher, Pedro Madruga, James Bentley, Thomas Belote, Luke @flexchar, Leonard Tan, Johann-Peter Hartmann, Illia Dulskyi, Fen Risland, Chadd, S_X, Jeff Scroggin, Ken Nordquist, Sean Connelly, Artur Olbinski, Swaroop Kallakuri, Jack West, Ai Maven, David Ziegler, Russ Johnson, transmissions 11, John Villwock, Alps Aficionado, Clay Pascal, Viktor Bowallius, Subspace Studios, Rainer Wilmers, Trenton Dambrowitz, vamX, Michael Levine, 준교 김, Brandon Frisco, Kalila, Trailburnt, Randy H, Talal Aujan, Nathan Dryer, Vadim, 阿明, ReadyPlayerEmma, Tiffany J. Kim, George Stoitzev, Spencer Kim, Jerry Meng, Gabriel Tamborski, Cory Kujawski, Jeffrey Morgan, Spiking Neurons AB, Edmond Seymore, Alexandros Triantafyllidis, Lone Striker, Cap'n Zoog, Nikolai Manek, danny, ya boyyy, Derek Yates, usrbinkat, Mandus, TL, Nathan LeClaire, subjectnull, Imad Khwaja, webtim, Raven Klaugh, Asp the Wyvern, Gabriel Puliatti, Caitlyn Gatomon, Joseph William Delisle, Jonathan Leane, Luke Pendergrass, SuperWojo, Sebastain Graf, Will Dee, Fred von Graf, Andrey, Dan Guido, Daniel P. Andersen, Nitin Borwankar, Elle, Vitor Caleffi, biorpg, jjj, NimbleBox.ai, Pieter, Matthew Berman, terasurfer, Michael Davis, Alex, Stanislav Ovsiannikov
Thank you to all my generous patrons and donaters!
And thank you again to a16z for their generous grant.
Original model card: Open-Orca's LlongOrca 7B 16K
🐋 The First Llong Context Orca! 🐋
OpenOrca - LlongOrca - 7B - 16k
We have used our own OpenOrca dataset to fine-tune on top of LLongMA-2-7b-16k. This dataset is our attempt to reproduce the dataset generated for Microsoft Research's Orca Paper. We use OpenChat packing, trained with Axolotl.
This release is trained on a curated filtered subset of most of our GPT-4 augmented data. It is the same subset of our data as was used in our OpenOrcaxOpenChat-Preview2-13B model.
This release reveals that stacking our training on an existing long context fine-tuned model yields significant improvements to model performance. We measured this with BigBench-Hard and AGIEval results, finding ~134% of the base Llongma2-16k model's performance on average.
We have run extensive evaluations internally and expect this model to place number 4 on the HuggingFaceH4 Open LLM Leaderboard for 7B models, but with >99% performance of the first place and place number 1 for longer context 7B models.
We did this training as part of testing integration of OpenChat's MultiPack algorithm into the Axolotl trainer. MultiPack achieves 99.85% bin-packing efficiency on our dataset. This has significantly reduced training time, with efficiency improvement of 3-10X over traditional methods.

Want to visualize our full (pre-filtering) dataset? Check out our Nomic Atlas Map.
Many thanks to @EnricoShippole, @theemozilla, and @kaiokendev1 for the fine work on creating the LlongMA-2-7b-16k model this was trained on top of!
We are in-process with training more models, so keep a look out on our org for releases coming soon with exciting partners.
We will also give sneak-peak announcements on our Discord, which you can find here:
Prompt Template
We used OpenAI's Chat Markup Language (ChatML) format, with <|im_start|> and <|im_end|> tokens added to support this.
Example Prompt Exchange
<|im_start|>system
You are LlongOrca, a large language model trained by Alignment Lab AI. Write out your reasoning step-by-step to be sure you get the right answers!
<|im_end|>
<|im_start|>user
How are you<|im_end|>
<|im_start|>assistant
I am doing well!<|im_end|>
<|im_start|>user
How are you now?<|im_end|>
Evaluation
We have evaluated using the methodology and tools for the HuggingFace Leaderboard, and find that we have significantly improved upon the base long context model. As well, we should place #4 among all 7B models (and #1 for a model with long context) at release time!
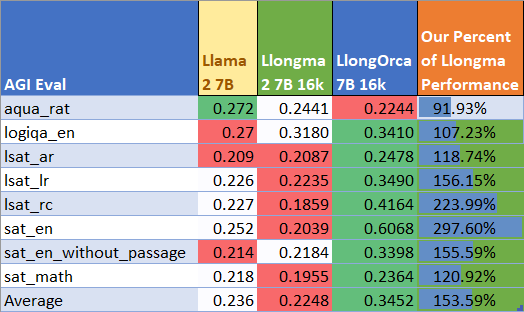
AGIEval Performance
We present our performance on AGI Eval in comparison to base Llama2-7B and to Llongma2-7b-16k, which we trained on top of. This demonstrates the benefits of stacking OpenOrca dataset training on existing models. Most notably, there is a very dramatic improvement of nearly 3X in the English writing performance.
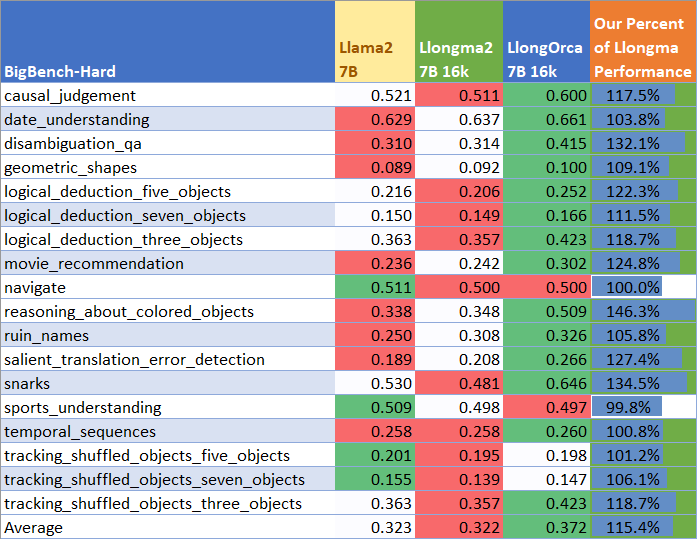
BigBench-Hard Performance
We present our performance on BigBench-Hard in comparison to base Llama2-7B and to Llongma2-7b-16k, which we trained on top of. This demonstrates the benefits of stacking OpenOrca dataset training on existing models.
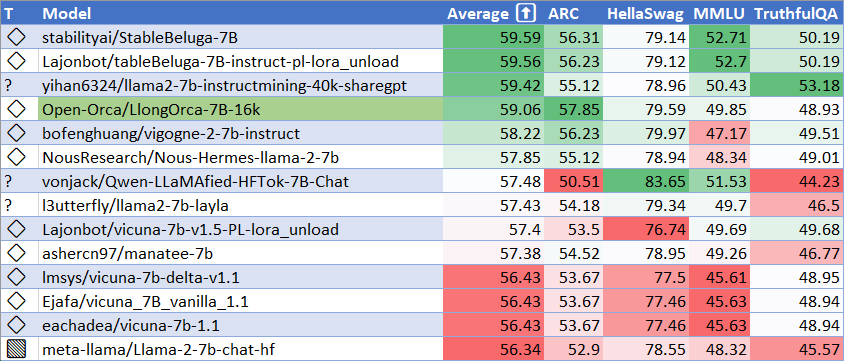
HuggingFaceH4 Open LLM Leaderboard Performance
We have run our own tests using parameters matching the HuggingFaceH4 Open LLM Leaderboard evals.
We place #4 for all 7B models at release time, and #1 for long context models.
Dataset
We used a curated, filtered selection of most of the GPT-4 augmented data from our OpenOrca dataset, which aims to reproduce the Orca Research Paper dataset. Further details of our curation practices will be forthcoming with our full model releases.
Training
We trained with 8x A6000-48GB (first-gen) GPUs for 37 hours, completing 4 epochs of full fine tuning on our dataset in one training run.
Commodity cost was ~$200.
Axolotl training parameters can be found in configs/oo7b.yml.
We used the packing-attn branch of Axolotl during training.
Citation
@software{lian2023llongorca7b,
title = {LlongOrca7B: Llama2-7B Model Instruct-tuned for Long Context on Filtered OpenOrcaV1 GPT-4 Dataset},
author = {Wing Lian and Bleys Goodson and Guan Wang and Eugene Pentland and Austin Cook and Chanvichet Vong and "Teknium"},
year = {2023},
publisher = {HuggingFace},
journal = {HuggingFace repository},
howpublished = {\url{https://https://huggingface.co/Open-Orca/LlongOrca-7B-16k},
}
@software{openchat,
title = {{OpenChat: Advancing Open-source Language Models with Imperfect Data}},
author = {Wang, Guan and Cheng, Sijie and Yu, Qiying and Liu, Changling},
doi = {10.5281/zenodo.8105775},
url = {https://github.com/imoneoi/openchat},
version = {pre-release},
year = {2023},
month = {7},
}
@misc{mukherjee2023orca,
title={Orca: Progressive Learning from Complex Explanation Traces of GPT-4},
author={Subhabrata Mukherjee and Arindam Mitra and Ganesh Jawahar and Sahaj Agarwal and Hamid Palangi and Ahmed Awadallah},
year={2023},
eprint={2306.02707},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL}
}
@misc{longpre2023flan,
title={The Flan Collection: Designing Data and Methods for Effective Instruction Tuning},
author={Shayne Longpre and Le Hou and Tu Vu and Albert Webson and Hyung Won Chung and Yi Tay and Denny Zhou and Quoc V. Le and Barret Zoph and Jason Wei and Adam Roberts},
year={2023},
eprint={2301.13688},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.AI}
}
@misc{touvron2023llama,
title={Llama 2: Open Foundation and Fine-Tuned Chat Models},
author={Hugo Touvron and Louis Martin and Kevin Stone and Peter Albert and Amjad Almahairi and Yasmine Babaei and Nikolay Bashlykov and Soumya Batra and Prajjwal Bhargava and Shruti Bhosale and Dan Bikel and Lukas Blecher and Cristian Canton Ferrer and Moya Chen and Guillem Cucurull and David Esiobu and Jude Fernandes and Jeremy Fu and Wenyin Fu and Brian Fuller and Cynthia Gao and Vedanuj Goswami and Naman Goyal and Anthony Hartshorn and Saghar Hosseini and Rui Hou and Hakan Inan and Marcin Kardas and Viktor Kerkez and Madian Khabsa and Isabel Kloumann and Artem Korenev and Punit Singh Koura and Marie-Anne Lachaux and Thibaut Lavril and Jenya Lee and Diana Liskovich and Yinghai Lu and Yuning Mao and Xavier Martinet and Todor Mihaylov and Pushkar Mishra and Igor Molybog and Yixin Nie and Andrew Poulton and Jeremy Reizenstein and Rashi Rungta and Kalyan Saladi and Alan Schelten and Ruan Silva and Eric Michael Smith and Ranjan Subramanian and Xiaoqing Ellen Tan and Binh Tang and Ross Taylor and Adina Williams and Jian Xiang Kuan and Puxin Xu and Zheng Yan and Iliyan Zarov and Yuchen Zhang and Angela Fan and Melanie Kambadur and Sharan Narang and Aurelien Rodriguez and Robert Stojnic and Sergey Edunov and Thomas Scialom},
year={2023},
eprint={2307.09288},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
}