base_model: deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-instruct
tags:
- instruct
- finetune
library_name: transformers
license: cc-by-sa-4.0
pipeline_tag: text-generation
Natural-SQL-7B by ChatDB
Natural-SQL-7B is a model with very strong performance in Text-to-SQL instructions, has an excellent understanding of complex questions, and outperforms models of the same size in its space.

ChatDB.ai | Notebook | Twitter
Benchmarks
Results on Novel Datasets not trained on via SQL-Eval
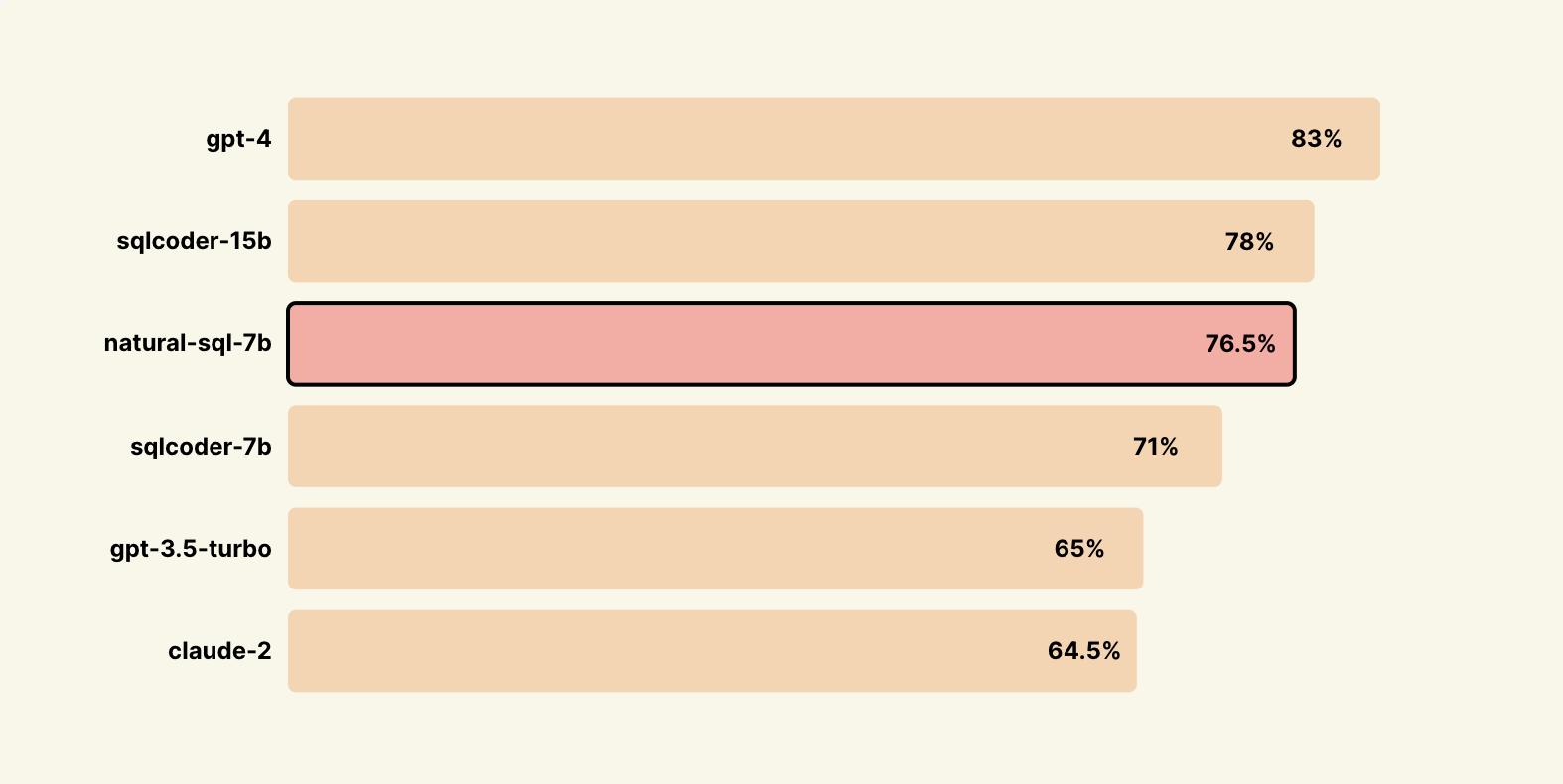
Big thanks to the defog team for open sourcing sql-eval👏
Natural-SQL also can handle complex, compound questions that other models typically struggle with. There is a more detailed writeup Here is a write up, small test done here.
Usage
Make sure you have the correct version of the transformers library installed:
pip install transformers==4.35.2
Loading the Model
Use the following Python code to load the model:
import torch
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("chatdb/natural-sql-7b")
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
"chatdb/natural-sql-7b",
device_map="auto",
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
)
License
The model weights are licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0, with extra guidelines for responsible use expanded from the original model's Deepseek license.
You're free to use and adapt the model, even commercially.
If you alter the weights, such as through fine-tuning, you must publicly share your changes under the same CC BY-SA 4.0 license.
Generating SQL
inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
generated_ids = model.generate(
**inputs,
num_return_sequences=1,
eos_token_id=100001,
pad_token_id=100001,
max_new_tokens=400,
do_sample=False,
num_beams=1,
)
outputs = tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
print(outputs[0].split("```sql")[-1])
Prompt Template
# Task
Generate a SQL query to answer the following question: `{natural language question}`
### PostgreSQL Database Schema
The query will run on a database with the following schema:
<SQL Table DDL Statements>
# SQL
Here is the SQL query that answers the question: `{natural language question}`
'''sql
Example SQL Output
Example Schemas
CREATE TABLE users (
user_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
username VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
password_hash TEXT NOT NULL,
created_at TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);
CREATE TABLE projects (
project_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
project_name VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
description TEXT,
start_date DATE,
end_date DATE,
owner_id INTEGER REFERENCES users(user_id)
);
CREATE TABLE tasks (
task_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
task_name VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
description TEXT,
due_date DATE,
status VARCHAR(50),
project_id INTEGER REFERENCES projects(project_id)
);
CREATE TABLE taskassignments (
assignment_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
task_id INTEGER REFERENCES tasks(task_id),
user_id INTEGER REFERENCES users(user_id),
assigned_date DATE NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);
CREATE TABLE comments (
comment_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
content TEXT NOT NULL,
created_at TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
task_id INTEGER REFERENCES tasks(task_id),
user_id INTEGER REFERENCES users(user_id)
);
Example SQL Outputs
Question: Show me the day with the most users joining
SELECT created_at::DATE AS day, COUNT(*) AS user_count
FROM users
GROUP BY day
ORDER BY user_count DESC
LIMIT 1;
Question: Show me the project that has a task with the most comments
SELECT p.project_name, t.task_name, COUNT(c.comment_id) AS comment_count
FROM projects p
JOIN tasks t ON p.project_id = t.project_id
JOIN comments c ON t.task_id = c.task_id
GROUP BY p.project_name, t.task_name
ORDER BY comment_count DESC
LIMIT 1;
Question: What is the ratio of users with gmail addresses vs without?
SELECT
SUM(CASE WHEN email ILIKE '%@gmail.com%' THEN 1 ELSE 0 END)::FLOAT / NULLIF(SUM(CASE WHEN email NOT ILIKE '%@gmail.com%' THEN 1 ELSE 0 END), 0) AS gmail_ratio
FROM
users;