license: apache-2.0
pipeline_tag: time-series-forecasting
tags:
- time series
- forecasting
- pretrained models
- foundation models
- time series foundation models
- time-series
Granite-TimeSeries-TTM-R2 Model Card

TinyTimeMixers (TTMs) are compact pre-trained models for Multivariate Time-Series Forecasting, open-sourced by IBM Research. With model sizes starting from 1M params, TTM (accepted in NeurIPS 24) introduces the notion of the first-ever “tiny” pre-trained models for Time-Series Forecasting.
TTM outperforms several popular benchmarks demanding billions of parameters in zero-shot and few-shot forecasting. TTMs are lightweight forecasters, pre-trained on publicly available time series data with various augmentations. TTM provides state-of-the-art zero-shot forecasts and can easily be fine-tuned for multi-variate forecasts with just 5% of the training data to be competitive. Refer to our paper for more details.
The current open-source version supports point forecasting use-cases specifically ranging from minutely to hourly resolutions (Ex. 10 min, 15 min, 1 hour.).
Note that zeroshot, fine-tuning and inference tasks using TTM can easily be executed in 1 GPU machine or in laptops too!!
TTM-R2 comprises TTM variants pre-trained on larger pretraining datasets (~700M samples). We have another set of TTM models released under TTM-R1 trained on ~250M samples
which can be accessed from here. In general, TTM-R2 models perform better than TTM-R1 models as they are
trained on larger pretraining dataset. In standard benchmarks, TTM-R2 outperform TTM-R1 by over 15%. However, the choice of R1 vs R2 depends on your target data distribution. Hence requesting users to try both
R1 and R2 variants and pick the best for your data.
Model Description
TTM falls under the category of “focused pre-trained models”, wherein each pre-trained TTM is tailored for a particular forecasting setting (governed by the context length and forecast length). Instead of building one massive model supporting all forecasting settings, we opt for the approach of constructing smaller pre-trained models, each focusing on a specific forecasting setting, thereby yielding more accurate results. Furthermore, this approach ensures that our models remain extremely small and exceptionally fast, facilitating easy deployment without demanding a ton of resources.
Hence, in this model card, we release several pre-trained TTMs that can cater to many common forecasting settings in practice.
Each pre-trained model will be released in a different branch name in this model card. Kindly access the required model using our getting started notebook mentioning the branch name.
Model Releases (along with the branch name where the models are stored):
512-96-r2: Given the last 512 time-points (i.e. context length), this model can forecast up to the next 96 time-points (i.e. forecast length) in future. (branch name: main)
1024-96-r2: Given the last 1024 time-points (i.e. context length), this model can forecast up to the next 96 time-points (i.e. forecast length) in future. (branch name: 1024-96-r2) [[Benchmarks]]
1536-96-r2: Given the last 1536 time-points (i.e. context length), this model can forecast up to the next 96 time-points (i.e. forecast length) in future. (branch name: 1536-96-r2)
Likewise, we have models released for forecast lengths up to 720 timepoints. The branch names for these are as follows:
512-192-r2,1024-192-r2,1536-192-r2,512-336-r2,512-336-r2,1024-336-r2,1536-336-r2,512-720-r2,1024-720-r2,1536-720-r2Please use the [get_model] utility to automatically select the required model based on your input context length and forecast length requirement.
We currently allow 3 context lengths (512, 1024 and 1536) and 4 forecast lengths (96, 192, 336, 720). Users need to provide one of the 3 allowed context lengths as input. but can provide any forecast lengths up to 720 in get_model() to get the required model.
Model Capabilities with example scripts
The below model scripts can be used for any of the above TTM models. Please update the HF model URL and branch name in the from_pretrained call appropriately to pick the model of your choice.
- Getting Started [colab]
- Zeroshot Multivariate Forecasting [Example]
- Finetuned Multivariate Forecasting:
- Channel-Independent Finetuning [Example 1] [Example 2]
- Channel-Mix Finetuning [Example]
- New Releases (extended features released on October 2024)
- Finetuning and Forecasting with Exogenous/Control Variables [Example]
- Finetuning and Forecasting with static categorical features [Example: To be added soon]
- Rolling Forecasts - Extend forecast lengths via rolling capability. Rolling beyond 2*forecast_length is not recommended. [Example]
- Helper scripts for optimal Learning Rate suggestions for Finetuning [Example]
Benchmarks
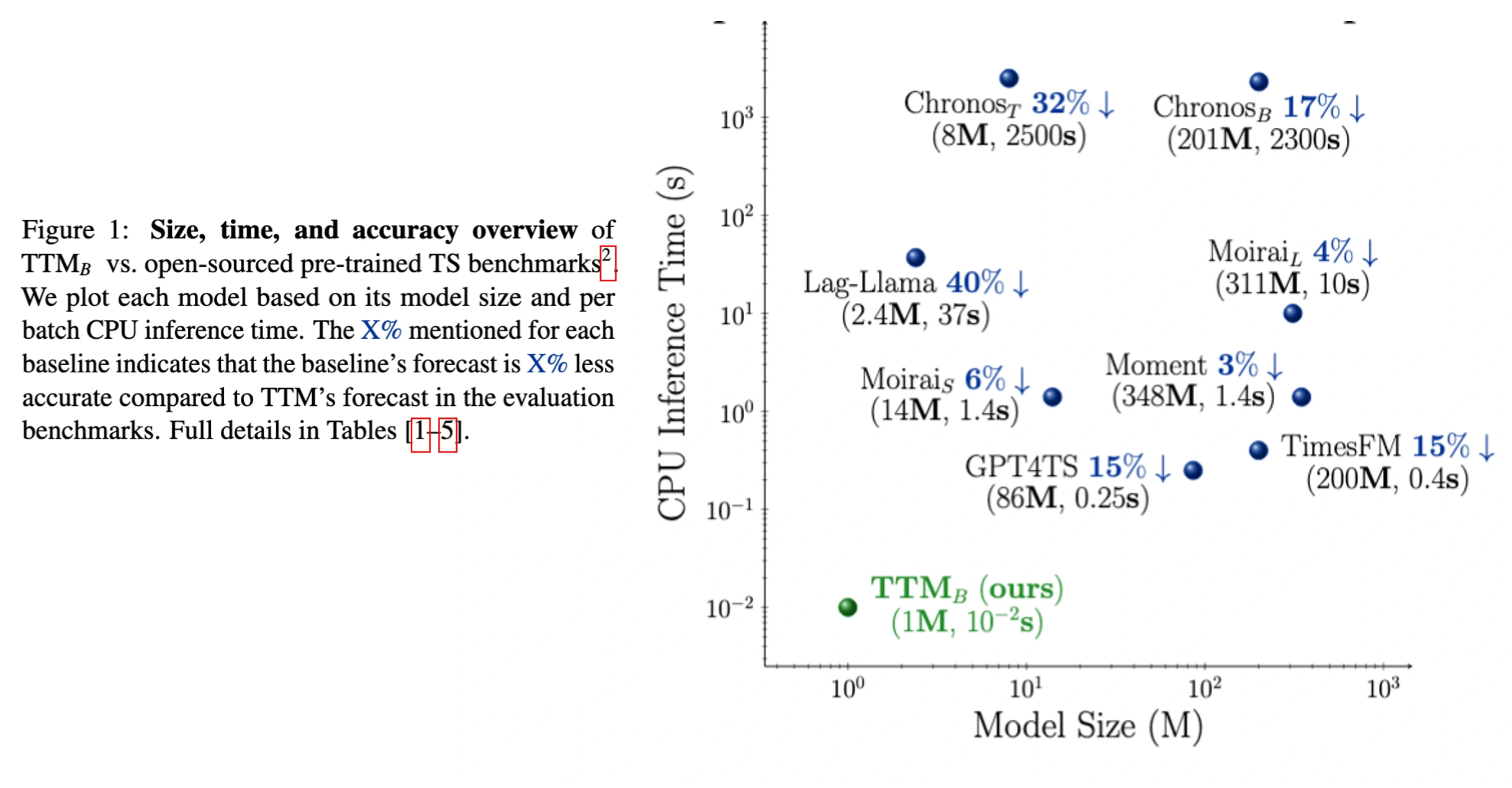
TTM outperforms popular benchmarks such as TimesFM, Moirai, Chronos, Lag-Llama, Moment, GPT4TS, TimeLLM, LLMTime in zero/fewshot forecasting while reducing computational requirements significantly. Moreover, TTMs are lightweight and can be executed even on CPU-only machines, enhancing usability and fostering wider adoption in resource-constrained environments. For more details, refer to our paper.
- TTM-B referred in the paper maps to the 512 context models.
- TTM-E referred in the paper maps to the 1024 context models.
- TTM-A referred in the paper maps to the 1536 context models.
Please note that the Granite TTM models are pre-trained exclusively on datasets with clear commercial-use licenses that are approved by our legal team. As a result, the pre-training dataset used in this release differs slightly from the one used in the research paper, which may lead to minor variations in model performance as compared to the published results. Please refer to our paper for more details.
Benchmarking Scripts: here
Recommended Use
- Users have to externally standard scale their data independently for every channel before feeding it to the model (Refer to TSP, our data processing utility for data scaling.)
- The current open-source version supports only minutely and hourly resolutions(Ex. 10 min, 15 min, 1 hour.). Other lower resolutions (say weekly, or monthly) are currently not supported in this version, as the model needs a minimum context length of 512 or 1024.
- Enabling any upsampling or prepending zeros to virtually increase the context length for shorter-length datasets is not recommended and will impact the model performance.
Model Details
For more details on TTM architecture and benchmarks, refer to our paper.
TTM-1 currently supports 2 modes:
Zeroshot forecasting: Directly apply the pre-trained model on your target data to get an initial forecast (with no training).
Finetuned forecasting: Finetune the pre-trained model with a subset of your target data to further improve the forecast.
Since, TTM models are extremely small and fast, it is practically very easy to finetune the model with your available target data in few minutes to get more accurate forecasts.
The current release supports multivariate forecasting via both channel independence and channel-mixing approaches. Decoder Channel-Mixing can be enabled during fine-tuning for capturing strong channel-correlation patterns across time-series variates, a critical capability lacking in existing counterparts.
In addition, TTM also supports exogenous infusion and categorical data infusion.
Model Sources
- Repository: https://github.com/ibm-granite/granite-tsfm/tree/main/tsfm_public/models/tinytimemixer
- Paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2401.03955.pdf
Blogs and articles on TTM:
- Refer to our wiki
Uses
Automatic Model selection
def get_model(
model_path,
model_name: str = "ttm",
context_length: int = None,
prediction_length: int = None,
freq_prefix_tuning: bool = None,
**kwargs,
):
TTM Model card offers a suite of models with varying context_length and forecast_length combinations.
This wrapper automatically selects the right model based on the given input context_length and prediction_length abstracting away the internal
complexity.
Args:
model_path (str):
HF model card path or local model path (Ex. ibm-granite/granite-timeseries-ttm-r1)
model_name (*optional*, str)
model name to use. Allowed values: ttm
context_length (int):
Input Context length. For ibm-granite/granite-timeseries-ttm-r1, we allow 512 and 1024.
For ibm-granite/granite-timeseries-ttm-r2 and ibm/ttm-research-r2, we allow 512, 1024 and 1536
prediction_length (int):
Forecast length to predict. For ibm-granite/granite-timeseries-ttm-r1, we can forecast upto 96.
For ibm-granite/granite-timeseries-ttm-r2 and ibm/ttm-research-r2, we can forecast upto 720.
Model is trained for fixed forecast lengths (96,192,336,720) and this model add required `prediction_filter_length` to the model instance for required pruning.
For Ex. if we need to forecast 150 timepoints given last 512 timepoints using model_path = ibm-granite/granite-timeseries-ttm-r2, then get_model will select the
model from 512_192_r2 branch and applies prediction_filter_length = 150 to prune the forecasts from 192 to 150. prediction_filter_length also applies loss
only to the pruned forecasts during finetuning.
freq_prefix_tuning (*optional*, bool):
Future use. Currently do not use this parameter.
kwargs:
Pass all the extra fine-tuning model parameters intended to be passed in the from_pretrained call to update model configuration.
# Load Model from HF Model Hub mentioning the branch name in revision field
model = TinyTimeMixerForPrediction.from_pretrained(
"https://huggingface.co/ibm-granite/granite-timeseries-ttm-r2", revision="main"
)
or
from tsfm_public.toolkit.get_model import get_model
model = get_model(
model_path="https://huggingface.co/ibm-granite/granite-timeseries-ttm-r2",
context_length=512,
prediction_length=96
)
# Do zeroshot
zeroshot_trainer = Trainer(
model=model,
args=zeroshot_forecast_args,
)
)
zeroshot_output = zeroshot_trainer.evaluate(dset_test)
# Freeze backbone and enable few-shot or finetuning:
# freeze backbone
for param in model.backbone.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
finetune_model = get_model(
model_path="https://huggingface.co/ibm-granite/granite-timeseries-ttm-r2",
context_length=512,
prediction_length=96,
# pass other finetune params of decoder or head
head_dropout = 0.2
)
finetune_forecast_trainer = Trainer(
model=model,
args=finetune_forecast_args,
train_dataset=dset_train,
eval_dataset=dset_val,
callbacks=[early_stopping_callback, tracking_callback],
optimizers=(optimizer, scheduler),
)
finetune_forecast_trainer.train()
fewshot_output = finetune_forecast_trainer.evaluate(dset_test)
Training Data
The r2 TTM models were trained on a collection of datasets as follows:
- Australian Electricity Demand: https://zenodo.org/records/4659727
- Australian Weather: https://zenodo.org/records/4654822
- Bitcoin dataset: https://zenodo.org/records/5122101
- KDD Cup 2018 dataset: https://zenodo.org/records/4656756
- London Smart Meters: https://zenodo.org/records/4656091
- Saugeen River Flow: https://zenodo.org/records/4656058
- Solar Power: https://zenodo.org/records/4656027
- Sunspots: https://zenodo.org/records/4654722
- Solar: https://zenodo.org/records/4656144
- US Births: https://zenodo.org/records/4656049
- Wind Farms Production data: https://zenodo.org/records/4654858
- Wind Power: https://zenodo.org/records/4656032
- PEMSD3, PEMSD4, PEMSD7, PEMSD8, PEMS_BAY: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1g5v2Gq1tkOq8XO0HDCZ9nOTtRpB6-gPe
- LOS_LOOP: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1g5v2Gq1tkOq8XO0HDCZ9nOTtRpB6-gPe
Citation
Kindly cite the following paper, if you intend to use our model or its associated architectures/approaches in your work
BibTeX:
@inproceedings{ekambaram2024tinytimemixersttms,
title={Tiny Time Mixers (TTMs): Fast Pre-trained Models for Enhanced Zero/Few-Shot Forecasting of Multivariate Time Series},
author={Vijay Ekambaram and Arindam Jati and Pankaj Dayama and Sumanta Mukherjee and Nam H. Nguyen and Wesley M. Gifford and Chandra Reddy and Jayant Kalagnanam},
booktitle={Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2024)},
year={2024},
}
Model Card Authors
Vijay Ekambaram, Arindam Jati, Pankaj Dayama, Wesley M. Gifford, Sumanta Mukherjee, Chandra Reddy and Jayant Kalagnanam
IBM Public Repository Disclosure:
All content in this repository including code has been provided by IBM under the associated open source software license and IBM is under no obligation to provide enhancements, updates, or support. IBM developers produced this code as an open source project (not as an IBM product), and IBM makes no assertions as to the level of quality nor security, and will not be maintaining this code going forward.