pipeline_tag: text-generation
tags:
- text-generation-inference
- backpack
- backpackmodel
library_name: transformers
license: apache-2.0
datasets:
- openwebtext
language:
- en
Model Card for Backpack-GPT2
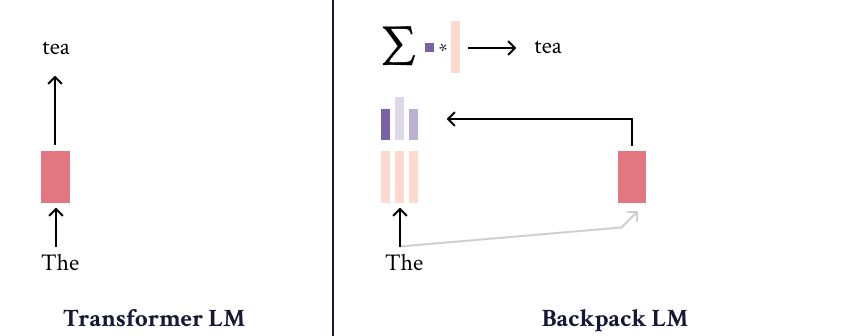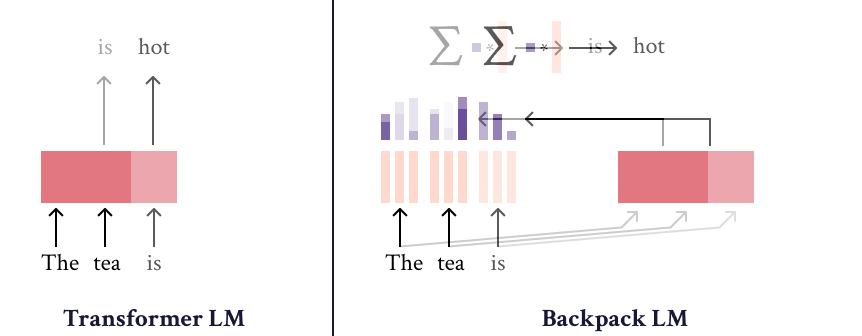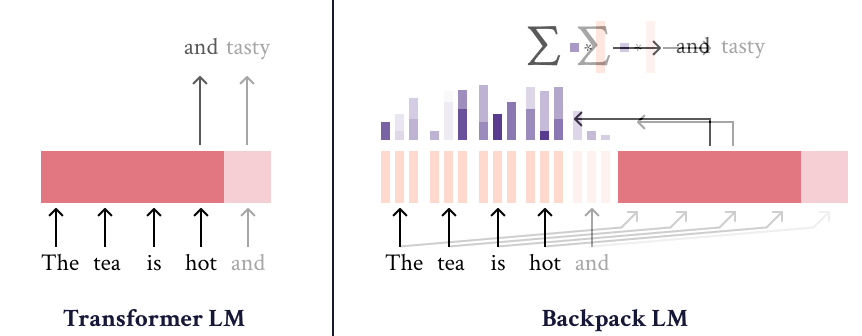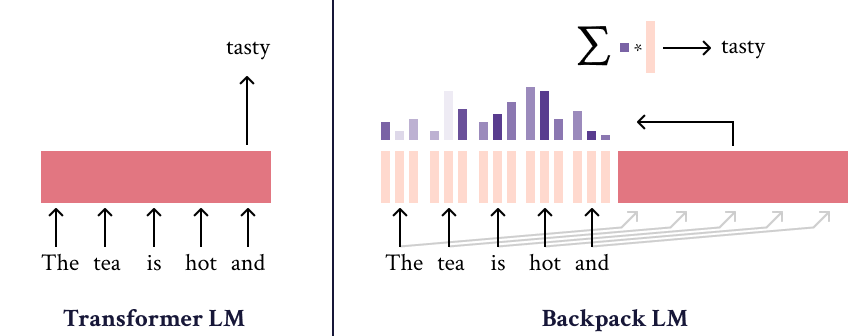
The Backpack-GPT2 language model is an instance of the Backpack architecture, intended to combine strong modeling performance with an interface for interpretability and control. Most details about this model and its training should be accessed in the paper, Backpack Language Models.
See also backpackmodels.science.
Table of Contents
- Model Card for Backpack-GPT2
- Table of Contents
- Model Details
- Uses
- Bias, Risks, and Limitations
- Training Details
- Environmental Impact
- Technical Specifications [optional]
- Citation
- Model Card Authors [optional]
- Model Card Contact
- How to Get Started with the Model
Model Details
Model Description
The Backpack-GPT2 is a Backpack-based language model, an architecture intended to combine strong modeling performance with an interface for interpretability and control.
- Developed by: John Hewitt, John Thickstun, Christopher D. Manning, Percy Liang
- Shared by [Optional]: More information needed
- Model type: Language model
- Language(s) (NLP): en
- License: apache-2.0
- Resources for more information:
Uses
This model is intended for use in the study and development of increasingly interpretable methods in natural language processing. It is not directly fit for any production use.
Bias, Risks, and Limitations
Significant research has explored bias and fairness issues with language models (see, e.g., Sheng et al. (2021) and Bender et al. (2021)). Predictions generated by the model may include disturbing and harmful stereotypes across protected classes; identity characteristics; and sensitive, social, and occupational groups. This model in particular is limited in its capabilities, and with a brand new architecture, less is known about its biases than, e.g., Transformer-based models.
Training Details
Training Data
This model was trained on the OpenWebText corpus.
Training Procedure
This model was trained for 100k gradient steps with a batch size of 512k tokens and a linearly decaying learning rate from 6e-4 to zero, with a linear warmup of 5k steps.
Environmental Impact
- Hardware Type: 4 A100 GPUs (40G)
- Hours used: Roughly 4 days.
- Cloud Provider: Stanford compute.
- Compute Region: Stanford energy grid.
Model Architecture and Objective
This model was trained to minimize the cross-entropy loss, and is a Backpack language model.
Compute Infrastructure
This model was trained on a slurm cluster.
Hardware
This model was trained on 4 A100s.
Software
This model was trained with FlashAttention and PyTorch
Citation
BibTeX:
@InProceedings{hewitt2023backpack,
author = "Hewitt, John and Thickstun, John and Manning, Christopher D. and Liang, Percy",
title = "Backpack Language Models",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the Association for Computational Linguistics",
year = "2023",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
location = "Toronto, Canada",
}
Model Card Authors [optional]
John Hewitt
Model Card Contact
How to Get Started with the Model
import torch
import transformers
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
model_id = "stanfordnlp/backpack-gpt2"
config = transformers.AutoConfig.from_pretrained(model_id, trust_remote_code=True)
torch_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id, config=config, trust_remote_code=True)
torch_model.eval()
input = torch.randint(0, 50264, (1, 512), dtype=torch.long)
torch_out = torch_model(
input,
position_ids=None,
)
torch_out = torch.nn.functional.softmax(torch_out.logits, dim=-1)
print(torch_out)
Click to expand
More information needed